Why Sprinkler Systems Matter More Than Ever
When discussing fire protection systems, one technology consistently stands out as a life-saving measure: the sprinkler system. Globally recognized as a cornerstone of fire suppression, sprinklers are designed to detect, control, and extinguish fires before they grow uncontrollably. In Saudi Arabia, their importance is amplified by a growing emphasis on civil defense standards, infrastructure modernization, and the country’s Vision 2030 initiatives aimed at raising safety benchmarks across industries.
Sprinkler systems are not just about compliance with rules; they represent the first line of defense in safeguarding lives, assets, and business continuity. In a nation experiencing rapid urban development where commercial towers, residential complexes, and industrial facilities are on the rise the question is no longer whether to install sprinklers but rather which system is best suited to a specific building type.
What Is a Sprinkler System and How Does It Work?
A sprinkler system is an integrated network of pipes, valves, and sprinkler heads connected to a reliable water source. When the temperature around a sprinkler head reaches a critical threshold typically caused by flames or rising heat the glass bulb or fusible element inside breaks. This releases water directly over the affected area, containing or extinguishing the fire at its earliest stage.
Unlike common misconceptions, sprinklers do not all activate at once. Each head operates independently, meaning only the area exposed to fire receives water. This precise activation reduces property damage while ensuring rapid intervention before the fire spreads.
Globally, studies show that buildings equipped with sprinklers experience an over 80% reduction in fire-related fatalities and property damage compared to those without. In Saudi Arabia, these numbers align with the government’s push to prioritize fire safety compliance in both public and private sectors.
Types of Sprinkler Systems Used in Saudi Arabia
Wet Pipe Systems
The most common configuration, wet pipe systems keep water constantly in the pipes. They are reliable, simple to maintain, and effective for environments where freezing is not a concern.
Dry Pipe Systems
Instead of water, dry systems fill pipes with compressed air or nitrogen. Once triggered, the air is released, allowing water to flow. These are typically used in colder climates or facilities where pipes may be exposed to freezing temperatures.
Pre-Action Systems
Designed for sensitive environments like data centers or museums, pre-action systems require two triggers: detection by a fire alarm and activation of the sprinkler head. This dual layer minimizes accidental water discharge.
Deluge Systems
In high-risk areas such as petrochemical facilities, deluge systems use open sprinkler heads that release water simultaneously when triggered. This configuration offers aggressive suppression for large-scale hazards.
Selecting the Right Sprinkler System for Your Building
Choosing the correct sprinkler system depends on hazard classification, building type, and occupancy load. For example:
- A residential apartment may use wet pipe systems for simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- A server room or archive facility would favor pre-action systems to minimize water damage risks.
- A petrochemical plant would demand deluge systems for large-scale hazard control.
DarAlhmaya emphasizes that system selection must always align with Saudi Building Code requirements and NFPA 13 standards, ensuring both local and international compliance.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia enforces strict civil defense standards to guarantee public safety in line with global best practices. The key pillars of regulation include:
Civil Defense Oversight
The Saudi Civil Defense Authority requires all new and existing buildings to undergo compliance checks. This includes not just the installation but also periodic maintenance of sprinkler systems.
Saudi Building Code (SBC)
The SBC mandates design, layout, and performance specifications for fire protection systems, ensuring alignment with local risks and environmental conditions.
NFPA 13 Compliance
Internationally recognized, NFPA 13 sets standards for the installation of sprinkler systems. In Saudi Arabia, these standards are adopted and localized within the SBC framework, ensuring a globally benchmarked approach to fire safety.
The Cost of Non-Compliance
For businesses, failing to comply with sprinkler regulations can lead to penalties, suspension of licenses, or even closure orders. More importantly, it exposes employees, customers, and valuable assets to catastrophic risks.
According to the Saudi Civil Defense Authority, inspections are carried out regularly, and violations can quickly escalate into financial and reputational damage. For organizations aiming to align with Vision 2030, compliance is not only a legal requirement but also a corporate responsibility.
The Role of DarAlhmaya in Sprinkler System Compliance
As a contractor specialized in fire protection systems, DarAlhmaya ensures that every project meets the highest safety benchmarks. By combining technical expertise with regulatory knowledge, DarAlhmaya helps clients navigate Saudi Arabia’s complex fire safety landscape.
From risk assessment and hazard analysis to installation and maintenance, the company provides end-to-end solutions that guarantee both building safety code compliance and long-term operational reliability. More details about their services are available on the DarAlhmaya services page.
Designing and Installing Sprinkler Systems in Saudi Arabia
Designing a sprinkler system is both a science and an art, requiring precision in calculations and a deep understanding of fire dynamics. In Saudi Arabia, system design follows the NFPA 13 standard, integrated into the Saudi Building Code to meet local conditions. A well-designed sprinkler system must balance efficiency with compliance, ensuring reliable performance during an emergency without over-engineering that drives costs unnecessarily.
The process begins with a hazard classification, determining the risk level of a building based on its purpose and occupancy. A warehouse filled with flammable goods presents different challenges compared to a residential tower. Each classification guides the spacing, flow rates, and type of sprinkler heads required. Engineers then perform hydraulic calculations to confirm that water supply, pump capacity, and pressure levels can deliver sufficient flow to extinguish fires under worst-case scenarios.
Occupancy and Hazard Considerations
Not all fires behave the same way, and understanding occupancy risks is central to system design. For example, a hospital demands a system that prioritizes reliability and minimal disruption to life safety operations. Meanwhile, industrial plants housing chemicals require more aggressive suppression systems, often supported by deluge configurations.
Saudi Arabia’s civil defense authorities stress the importance of aligning design choices with civil defense standards, meaning each installation must be tailored to the unique conditions of the facility. This ensures both fire risk management and long-term compliance with inspection requirements.
Layout, Spacing, and Obstruction Challenges
Beyond calculations, physical building conditions influence sprinkler design. Beams, lighting fixtures, and ventilation ducts can obstruct sprinkler spray patterns, reducing effectiveness. Engineers must carefully plan layouts to prevent shadow zones areas where water coverage is inadequate.
NFPA 13 outlines detailed spacing requirements for sprinklers, specifying distances from walls, ceilings, and obstructions. Meeting these guidelines is not optional; it is a mandatory part of building safety code compliance. Poorly planned layouts not only risk system failure during a fire but also expose building owners to penalties and liability.
Installation and Licensing Procedures
Installing a sprinkler system in Saudi Arabia requires contractors to hold a valid civil defense license, obtained only after demonstrating technical competence and compliance with safety regulations. Licensed contractors oversee the procurement of approved materials, proper pipe installation, and connection to reliable water supplies.
After installation, the system undergoes pressure tests and functional trials before being certified by civil defense inspectors. This rigorous process ensures that only systems meeting the highest performance benchmarks are approved for operational use. For clients, partnering with an experienced contractor like DarAlhmaya ensures a seamless path through licensing, installation, and certification without costly delays.
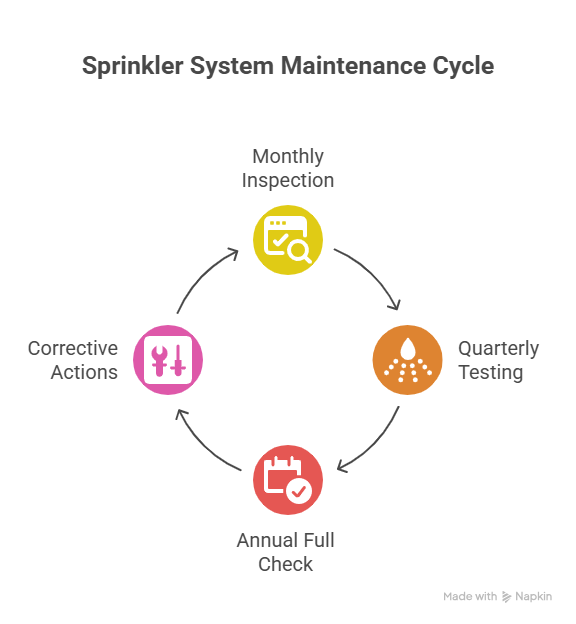
Maintenance: Keeping Sprinkler Systems Reliable
A sprinkler system is only as effective as its last inspection. Maintenance plays a pivotal role in ensuring that sprinklers function during emergencies. Saudi Arabia enforces ongoing compliance through NFPA 25, which specifies inspection, testing, and maintenance requirements.
Sprinkler systems should be visually inspected monthly to check for leaks, blockages, or tampering. Quarterly inspections test water flow alarms, control valves, and system monitoring devices. Annual maintenance involves full-scale testing, including pump performance and pressure verification. These tasks are not just technical checkboxes they directly impact the ability of the system to protect lives and property during a fire.
Common Problems and Their Solutions
Inspections often reveal recurring issues such as clogged sprinkler heads, corrosion in pipes, or faulty valves. Dust and paint accumulation on sprinkler heads can delay activation, while corrosion can reduce pipe diameter, restricting water flow. Addressing these problems promptly is essential to preserve system integrity.
Modern solutions, such as corrosion-resistant piping and smart monitoring devices, are increasingly being adopted in Saudi Arabia. These technologies provide real-time data on system health, allowing maintenance teams to respond proactively before minor issues escalate into failures.
Integration with Broader Fire Protection Systems
While sprinklers are powerful tools, they are not standalone solutions. The most effective safety strategies integrate sprinklers with alarms, smoke detectors, and building management systems. For instance, when a sprinkler activates, it should simultaneously trigger fire alarms, notify emergency response teams, and alert the central monitoring station.
This integrated approach aligns with fire prevention technology trends in Saudi Arabia, where smart buildings increasingly adopt digital platforms to oversee all safety systems from a single dashboard. Integration reduces response time and improves coordination during emergencies, ensuring that fire suppression is supported by evacuation and communication protocols.
Challenges Businesses Face in Sprinkler System Management
Despite the clear benefits, businesses in Saudi Arabia encounter challenges in managing sprinkler systems. Compliance with evolving codes can be complex, requiring frequent updates to existing infrastructure. Technical challenges also emerge in retrofitting older buildings, where ceiling heights, layouts, or water supply systems may not accommodate modern sprinkler designs easily.
Another recurring issue is the lack of trained personnel familiar with inspection protocols and emergency procedures. Without proper training, employees may overlook early warning signs of system malfunction or fail to follow correct procedures during fire incidents. Investing in training and awareness programs is therefore as critical as the system itself.
Innovations and Emerging Trends in Sprinkler Systems
As Saudi Arabia continues its path toward modernization, the technologies shaping fire safety are evolving rapidly. Sprinkler systems, once viewed as simple water-discharging devices, are now part of sophisticated fire protection systems integrated with smart building technologies. Recent innovations focus on enhancing efficiency, reliability, and data-driven performance, ensuring systems respond faster and last longer with minimal downtime.
One major trend is the adoption of smart monitoring solutions. These systems continuously track water pressure, valve positions, and pipe conditions, sending real-time alerts if abnormalities are detected. For facility managers, this proactive approach reduces reliance on manual inspections and ensures compliance with fire safety compliance standards. Coupled with cloud-based reporting, organizations can maintain precise records for civil defense audits, minimizing the risk of penalties.
Addressing Corrosion and Freeze Protection
Corrosion remains one of the biggest threats to sprinkler system longevity, particularly in regions with high humidity or harsh water conditions. In Saudi Arabia, where many facilities are exposed to extreme climates, corrosion-resistant pipes and coatings are gaining popularity. These innovations extend the life of systems while reducing costly replacements and downtime.
Freeze protection, while not as critical in Saudi Arabia as in colder regions, still matters in facilities with climate-controlled environments. New dry pipe and pre-action systems come with built-in freeze safeguards, ensuring reliability in diverse conditions. By adopting these advancements, businesses not only safeguard property but also reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Integration with Building Management Systems
The concept of connected safety has become increasingly prominent in modern construction. Sprinkler systems are no longer stand-alone tools but essential parts of broader commercial safety solutions. When integrated with building management systems (BMS), sprinklers can work in tandem with smoke detection, ventilation control, and emergency lighting to create a unified safety strategy.
For example, a sprinkler activation could trigger automatic elevator recalls, smoke exhaust fans, and alarm notifications across the building. This level of integration reduces response times and ensures smoother coordination between occupants and emergency responders. In Saudi Arabia, where high-rise developments dominate the skyline, such holistic approaches to safety are becoming industry best practice.
The Role of Training and Awareness
Even the most advanced sprinkler system cannot achieve its purpose without human readiness. Staff and occupants need to understand how systems function, how alarms coordinate with sprinklers, and what evacuation procedures to follow. In many fire incidents, delays occur not because the sprinklers fail but because people hesitate or misuse available safety systems.
DarAlhmaya emphasizes ongoing training as part of its service model. Through fire drills, awareness campaigns, and tailored educational programs, organizations can ensure that employees know their roles during emergencies. This aligns with both civil defense standards and Vision 2030’s broader goal of enhancing safety culture across industries.
Challenges Ahead for Businesses
While innovation offers new tools, challenges remain. Regulatory updates demand constant vigilance, as businesses must adapt to new codes and inspection protocols. Retrofitting older buildings with advanced sprinklers often involves significant cost and logistical planning. Moreover, keeping up with global standards like NFPA 13 while ensuring local compliance with the Saudi Building Code can overwhelm unprepared organizations.
Another challenge lies in balancing cost with performance. Businesses sometimes opt for the cheapest solutions, only to face failures during inspections or actual emergencies. Partnering with experienced contractors such as DarAlhmaya helps mitigate these risks by ensuring both technical excellence and regulatory alignment from the start.
Looking to the Future: Sprinklers in Vision 2030
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 places safety and sustainability at the heart of its development plans. Sprinkler systems will continue to play a vital role in supporting safer communities, especially as urbanization accelerates. New projects in healthcare, hospitality, and industrial sectors will demand high-performance sprinklers aligned with global best practices.
Moreover, as the Kingdom invests in smart city projects, sprinklers will increasingly connect with digital infrastructure, creating data-driven models for predictive maintenance and enhanced emergency response coordination. The combination of regulation, technology, and training positions Saudi Arabia as a leader in regional fire safety advancement.
Conclusion
Sprinkler systems are more than mechanical devices; they are essential guardians of life and property. In Saudi Arabia, their relevance is amplified by stringent civil defense standards, evolving technologies, and the rapid pace of urban growth. Choosing the right system, maintaining it diligently, and integrating it into wider safety frameworks ensures long-term protection and compliance.
DarAlhmaya continues to lead by offering end-to-end solutions that cover design, installation, and maintenance, all while keeping pace with innovations and regulatory updates. For organizations committed to safety, sprinklers are not optional investments they are indispensable components of a resilient and future-ready fire safety strategy.







