The Global Framework Shaping Saudi Arabia’s Fire Safety Vision
Fire safety has become a central pillar in Saudi Arabia’s journey toward modern infrastructure and sustainable development under Vision 2030. With rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and mega-projects transforming the landscape, the need for a unified approach to fire protection systems and civil defense regulations has never been more critical.
That’s where the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards come in a globally recognized set of codes and best practices designed to prevent fires, reduce risk, and protect both lives and property. These standards are not just international guidelines; they are an integral part of the Kingdom’s building safety codes and regulatory framework.
NFPA standards influence nearly every component of the built environment from fire suppression systems and alarm signaling to emergency preparedness and evacuation design. Their implementation in Saudi Arabia represents the nation’s strong commitment to fire safety compliance, innovation, and continuous improvement.
Understanding NFPA Standards and Their Relevance in Saudi Arabia
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) develops over 300 standards and codes that guide fire safety practices globally. In Saudi Arabia, these standards form the foundation for policies issued by the Saudi Civil Defense and the Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO).
The integration of NFPA standards ensures that every commercial, industrial, and residential development aligns with internationally recognized safety practices. This alignment enhances operational safety and boosts investor confidence in Saudi Arabia’s fast-growing infrastructure ecosystem.
To learn more about DARS’s expertise in applying these standards to real projects, visit the Services page on their official website.
The Key NFPA Standards Adopted in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia applies several NFPA standards tailored to different facility types and hazard levels. Among the most essential are:
NFPA 13: Installation of Sprinkler Systems
NFPA 13 governs the design, installation, and maintenance of sprinkler systems that form the backbone of fire suppression infrastructure. It ensures effective water distribution and flow control during emergencies, protecting both people and property in commercial and industrial settings.
NFPA 25: Inspection, Testing, and Maintenance of Water-Based Fire Protection Systems
NFPA 25 focuses on periodic safety inspection and maintenance routines for water-based systems. Regular inspections under this code ensure reliability and early detection of malfunctions, a crucial step in maintaining fire safety compliance.
NFPA 72: National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
This standard governs the installation and performance of fire alarm systems and emergency communications. In Saudi Arabia, it supports faster emergency alerts and coordination between building occupants, security teams, and the Civil Defense.
NFPA 101: Life Safety Code
NFPA 101 focuses on safe building design to prevent loss of life during fire incidents. It includes guidelines for evacuation, emergency lighting, and safe occupancy limits across different facility types from hospitals to high-rise towers.
NFPA 2001: Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems
This code is particularly relevant for data centers, control rooms, and sensitive environments. It specifies the use of clean agents that suppress fires without damaging critical equipment, ensuring both safety and sustainability.
Harmonizing NFPA Standards with Saudi Civil Defense Regulations
One of the most remarkable achievements in Saudi Arabia’s fire safety evolution is the harmonization of NFPA standards with local civil defense regulations and the Saudi Building Code (SBC). This integration simplifies compliance and ensures that both local contractors and global firms operate under a shared safety framework.
The Saudi Civil Defense mandates adherence to NFPA standards in construction permits, inspection approvals, and periodic audits. This harmonization also improves communication between engineers, authorities, and project owners, reducing delays and ensuring consistent fire protection systems across the Kingdom.
Organizations such as SASO and the National Center for Environmental Compliance further align international fire safety principles with the Kingdom’s unique environmental and operational conditions. The result is a national safety framework that’s robust, adaptable, and forward-looking.
Why NFPA Standards Matter for Vision 2030 Projects
Saudi Arabia’s giga-projects such as NEOM, The Red Sea Global, and Qiddiya are at the forefront of integrating NFPA standards to meet world-class safety benchmarks. These projects not only require innovative architecture and technology but also uncompromising fire protection design.
NFPA standards serve as the blueprint for:
- Fire prevention solutions that minimize risk across large-scale developments.
- Fire risk assessment processes that guide every phase of construction and operation.
- Emergency preparedness plans ensure quick, organized responses in case of fire incidents.
For example, NFPA 101 plays a pivotal role in defining safe egress routes in high-rise developments like the King Abdullah Financial District, while NFPA 13 and NFPA 72 ensure that fire suppression and alarm systems are optimized for real-time coordination.
This alignment of safety practices with Vision 2030 goals reflects the Kingdom’s dedication to protecting not only its people but also the economic investments shaping its future.
Enhancing Emergency Response and Public Safety
At its core, the purpose of NFPA standards is to improve emergency preparedness and response efficiency. Whether it’s a shopping mall in Riyadh or an industrial complex in Yanbu, these standards outline clear procedures for alarm activation, evacuation, and incident management.
By standardizing fire alarm systems and communication protocols, NFPA 72 ensures that emergency responders receive accurate information quickly, saving valuable time during crises. Furthermore, NFPA 25 enhances system reliability by requiring periodic testing and recordkeeping, which in turn enables faster, more effective firefighting operations.
Saudi Arabia’s emphasis on these standards complements national initiatives under Vision 2030 that aim to modernize infrastructure while ensuring maximum public safety.
For additional details about inspection and compliance, readers can explore DARS’s Risk Manager service page, which outlines professional support for maintaining high fire safety standards across various industries.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in NFPA Compliance
Modern technologies have revolutionized how NFPA standards are implemented and monitored. In Saudi Arabia, many new projects now integrate smart sensors, IoT-based detection systems, and cloud-based inspection records to maintain fire safety compliance more efficiently.
Systems such as intelligent sprinkler networks (aligned with NFPA 13) or automated alert notifications (based on NFPA 72) ensure real-time performance tracking. This data-driven approach enhances system readiness while reducing manual errors, a major leap toward sustainable safety management.
Furthermore, environmentally friendly fire suppression systems aligned with NFPA 2001 use clean agents that reduce environmental impact and meet the Kingdom’s sustainability goals. These solutions are particularly relevant for sensitive environments like hospitals, data centers, and laboratories.
Challenges in Implementing NFPA Standards in Saudi Arabia
Despite remarkable progress, the road to full NFPA compliance in Saudi Arabia isn’t without challenges. The Kingdom faces specific environmental and logistical factors that require careful adaptation.
One major challenge involves system durability in harsh desert climates, where high temperatures can affect fire protection systems performance. Another issue lies in the shortage of trained local technicians fully certified in NFPA-specific training, particularly for inspection and maintenance.
Cultural and operational nuances also require flexibility for example, designing evacuation plans suitable for mixed-use developments or high-occupancy venues during peak hours.
However, ongoing training programs, technology integration, and public-private collaboration continue to address these gaps, ensuring smoother implementation across the board.
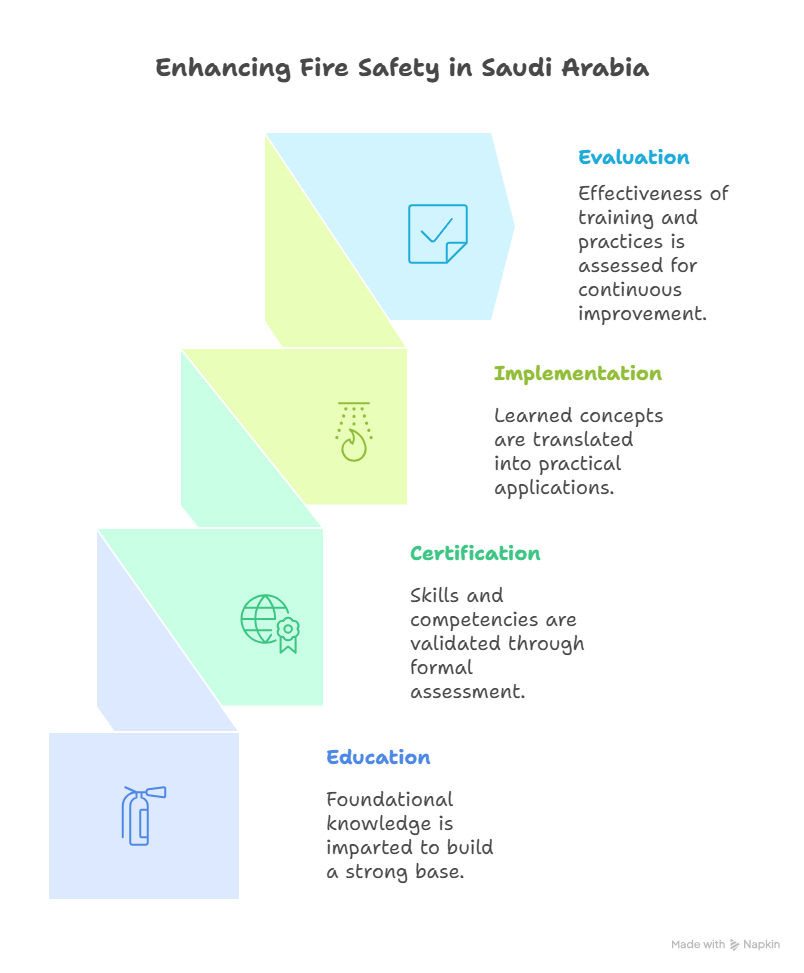
The Path Forward: Education and Continuous Improvement
Education remains the cornerstone of effective NFPA adoption. Saudi Arabia has made significant investments in training initiatives, including specialized certification programs in partnership with the NFPA, Saudi Civil Defense, and local universities.
These efforts equip engineers, inspectors, and contractors with the knowledge needed to interpret and apply NFPA standards correctly. Moreover, regular workshops, conferences, and events such as the Intersec Saudi Arabia exhibition encourage ongoing dialogue about innovation in fire safety.
Organizations like DARS are leading this movement by offering expert consultation, system evaluation, and continuous improvement programs for both private and public sectors.
NFPA Standards in Practice: Shaping the Kingdom’s Safety Landscape
Beyond compliance, these standards have become a framework for engineering excellence ensuring that every new building, industrial plant, or public facility is designed with precision, inspected with consistency, and maintained for longevity.
The growing complexity of construction projects, from smart cities to logistics hubs, requires a unified language for safety. NFPA standards provide that language, one that engineers, regulators, and contractors understand globally. When implemented effectively, they minimize ambiguity, reduce approval delays, and improve communication across project teams.
How NFPA Standards Influence Construction Workflows
In modern construction, applying NFPA standards begins long before the foundation is poured. Architects and consultants incorporate NFPA 13, NFPA 72, and NFPA 101 requirements directly into their designs, ensuring proper system spacing, evacuation routes, and fire compartmentation.
During the execution phase, certified contractors follow detailed installation procedures for sprinkler systems, alarms, and suppression networks. Each material used from pipes to control valves must comply with NFPA-listed product specifications. This level of rigor guarantees uniformity and reliability across all sites, regardless of scale.
Moreover, adherence to NFPA guidelines during the design and construction phase significantly simplifies the civil defense approval process. Projects that align with these standards from the start often experience smoother handovers and faster occupancy permits. For contractors and developers, compliance is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s a symbol of credibility and quality in Saudi Arabia’s evolving construction market.
Inspection and Maintenance: The Continuous Cycle of Compliance
Compliance doesn’t end when construction is complete in fact, that’s where it truly begins. NFPA 25 outlines the procedures for inspection, testing, and maintenance of fire protection systems, setting the rhythm for periodic system checks that ensure long-term reliability.
These inspections are vital for maintaining the integrity of sprinkler networks, alarms, and hydrants. Regular evaluations identify issues like corrosion, obstructions, or signal failures before they become critical. The Saudi Civil Defense mandates these inspections at specified intervals, and documented reports are essential for operational licensing.
Companies like DARS play a crucial role in this process, offering inspection and maintenance services grounded in NFPA best practices. Their approach prioritizes precision, transparency, and record-based verification all crucial for maintaining continuous fire safety compliance and minimizing risk exposure.
Training and Certification: Building Local Expertise
The widespread adoption of NFPA standards in Saudi Arabia has created a strong demand for local expertise. Engineers, technicians, and safety officers must not only understand the technical details of each standard but also know how to apply them under Saudi-specific conditions.
Training programs accredited by NFPA and local organizations, such as the Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO), are equipping professionals with practical skills in fire protection systems, fire alarm systems, and emergency preparedness.
This localized education ecosystem ensures that the Kingdom develops its own pipeline of certified specialists, reducing dependence on external consultants and building national capacity for sustainable safety management. Continuous learning and certification are now seen as vital career milestones in the fire safety sector.
NFPA Standards and Digital Transformation in Safety
Digitalization has become a key driver in achieving higher compliance accuracy. Smart fire protection systems, digital inspection checklists, and cloud-based compliance dashboards are now integrated into NFPA-aligned operations.
These technologies help facility managers track maintenance tasks, generate compliance reports automatically, and receive alerts for anomalies in sprinkler pressure or alarm circuits. With IoT integration, fire risk assessment has evolved from static evaluation to continuous, data-driven insight.
Saudi Arabia’s embrace of smart technologies reflects its Vision 2030 commitment to innovation and sustainability. NFPA standards complement this transformation by providing the technical foundation upon which digital safety ecosystems are built.
Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship in Fire Protection
Modern fire protection is no longer just about suppressing flames, it’s about doing so responsibly. The NFPA’s growing emphasis on sustainability has influenced the Kingdom’s fire safety strategy, especially regarding fire suppression agents and system efficiency.
Standards such as NFPA 2001 advocate for the use of clean agents that minimize environmental harm. In Saudi Arabia, this is particularly relevant in data centers and energy facilities where environmental compliance is closely monitored. These eco-friendly systems prevent contamination, conserve water, and support the Kingdom’s sustainability objectives aligned with Vision 2030.
DARS’s projects reflect this evolution. By implementing environmentally conscious fire prevention solutions, the company demonstrates that safety and sustainability can coexist seamlessly. Clients not only meet safety regulations but also contribute to the broader environmental goals of the nation.
NFPA’s Role in Enhancing Industrial Safety
Beyond commercial buildings, NFPA standards have reshaped safety protocols across Saudi Arabia’s industrial landscape. Oil refineries, manufacturing plants, and logistics centers all rely on these standards to mitigate the heightened risk of fire and explosion.
For instance, NFPA 30 covering flammable and combustible liquids is critical in facilities handling petroleum products. Similarly, NFPA 70 and NFPA 72 govern electrical safety and alarm communication, ensuring rapid response even in high-risk environments.
DARS collaborates with industrial clients to integrate NFPA-compliant fire systems that account for local climate challenges such as heat, sand exposure, and humidity. This expertise ensures that each installation remains functional and durable, even in extreme conditions.
Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
Saudi Arabia’s progress in fire safety compliance is the result of close collaboration between government authorities, private companies, and international bodies. The Saudi Civil Defense, SASO, and the NFPA work together to develop localized guidelines that preserve global quality while adapting to the Kingdom’s environment.
Private sector partners like DARS bridge this collaboration by translating regulatory frameworks into practical field implementation. Their experience across large-scale projects and their familiarity with both NFPA and Saudi Building Code (SBC) requirements make them valuable partners for developers seeking compliance and efficiency.
Such partnerships ensure that fire safety evolves alongside technological and architectural innovation rather than lagging behind it.
Case Example: NFPA Standards in Smart City Infrastructure
Smart city projects like NEOM and The Line represent the future of Saudi urban development, where safety is embedded in every digital and physical layer. NFPA standards guide the design of interconnected fire alarm systems, automated evacuation protocols, and integrated emergency response networks.
These systems use artificial intelligence to detect anomalies and coordinate real-time communication between security personnel and first responders. NFPA 72’s emphasis on reliable signaling infrastructure ensures that even in the most advanced urban setups, safety remains uncompromised.
The Economic Value of NFPA Compliance
Investing in NFPA-aligned fire safety measures goes beyond regulatory necessity; it’s a long-term financial strategy. Buildings that meet international fire safety compliance benchmarks often secure better insurance terms, lower maintenance costs, and higher asset valuation.
For investors and developers, NFPA compliance signals quality assurance and operational reliability. In an economy diversifying under Vision 2030, such reliability attracts global partners who prioritize risk management and sustainability.
Companies like DARS help clients recognize this value by designing systems that not only meet safety expectations but also contribute to the overall resilience and profitability of their properties.
The Future of NFPA Standardization in the Kingdom
As Saudi Arabia accelerates its infrastructure growth, the future of NFPA standardization is becoming even more vital. The Kingdom’s transition toward smart, sustainable cities demands systems that are not only compliant but also adaptive to emerging risks and technologies.
NFPA standards will continue to evolve alongside this transformation expanding their scope to include electric vehicle infrastructure, renewable energy facilities, and high-density urban zones. Each new update reflects a growing global understanding of how technology, design, and human behavior intersect to enhance fire safety outcomes.
Saudi Arabia’s ongoing alignment with the National Fire Protection Association ensures that both public and private sectors operate within a unified framework. This consistency fosters safer environments, stronger investor confidence, and better preparedness for the complex safety challenges of the future.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in Fire Safety
The next generation of fire protection systems will rely heavily on automation and predictive intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are redefining how fire risk assessment and safety inspection processes function.
Smart sensors can now detect abnormal heat patterns before ignition, while integrated alarm systems can pinpoint exact fire sources within seconds. Predictive maintenance tools, guided by data analytics, forecast potential failures before they happen, a concept already supported by NFPA 25’s focus on proactive inspection and testing.
For large developments like NEOM or The Red Sea Global, these technologies ensure that safety mechanisms work seamlessly with other digital infrastructure. NFPA’s emphasis on innovation guarantees that fire safety remains at the forefront of Saudi Arabia’s technological revolution.
Integrating Sustainability with Fire Protection
Sustainability has become more than an environmental goal; it’s now a design principle deeply embedded within NFPA’s philosophy. Future NFPA codes are increasingly prioritizing eco-conscious fire suppression systems, recyclable materials, and water-saving mechanisms that complement Saudi Arabia’s environmental strategy.
For example, clean agent systems under NFPA 2001 eliminate harmful emissions, protecting delicate electronics without leaving residue. Similarly, NFPA 13 supports efficient water distribution methods that minimize waste during emergencies. By combining these practices with green building certifications, the Kingdom ensures its safety infrastructure remains both effective and sustainable.
DARS continues to advance this mission by applying innovative technologies and eco-friendly materials across its projects. The company’s work demonstrates that environmental protection and fire safety compliance can coexist safeguarding both people and the planet.
The Growing Importance of Data and Documentation
In the era of smart regulation, data is becoming a cornerstone of fire safety management. NFPA-compliant systems now emphasize digital recordkeeping to document inspections, maintenance logs, and compliance reports in real time.
These records not only support transparency but also enable authorities like the Saudi Civil Defense to conduct faster audits and enforce standards more efficiently. Cloud-based compliance platforms are expected to become a legal requirement in the coming years, making digital readiness an essential part of any organization’s safety strategy.
By maintaining consistent digital documentation aligned with NFPA 25 and NFPA 72, organizations can significantly reduce operational risks while streamlining renewal processes for certifications and permits.
Global Collaboration and Knowledge Exchange
Saudi Arabia’s role in the global safety ecosystem continues to expand through partnerships with international institutions. Regular participation in NFPA conferences, technical committees, and knowledge exchange programs enables local experts to stay aligned with global trends.
This collaboration fosters innovation in fire prevention solutions, enhances training methodologies, and supports the adaptation of new NFPA codes to local contexts. As a result, the Kingdom not only benefits from international expertise but also contributes valuable regional insights especially on desert resilience, industrial safety, and large-scale infrastructure protection.
Organizations like DARS act as practical channels for these collaborations, implementing lessons learned from global partners into projects that reflect both international excellence and local relevance.
Education as the Foundation of a Safer Tomorrow
Sustainable fire safety depends on awareness from policy makers to building occupants. While regulations and systems form the structural layer of safety, education ensures that everyone understands their role within it.
NFPA 101 emphasizes occupant protection and evacuation design, but these measures are most effective when individuals are trained to act swiftly and responsibly. Workshops, fire drills, and awareness programs led by both government and private entities have proven instrumental in building a culture of safety across Saudi Arabia.
DARS continues to champion this approach by offering client training programs on emergency preparedness, evacuation procedures, and routine system checks. This educational outreach transforms compliance from a technical obligation into a shared community responsibility.
The Business Case for NFPA Adoption
Compliance with NFPA standards isn’t just about safety, it’s also a sound business decision. Organizations adhering to international building safety codes and civil defense regulations are viewed as reliable partners by insurers, investors, and global clients.
Fire safety failures can lead to enormous economic losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. By contrast, NFPA-certified systems enhance property value, improve operational continuity, and support sustainability reporting.
Many businesses in Saudi Arabia now recognize that NFPA compliance reflects operational maturity. For companies like DARS, this alignment goes beyond meeting legal expectations; it demonstrates leadership, professionalism, and commitment to excellence.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges Through Innovation
Even with strong adoption, practical challenges persist from aligning older buildings with new codes to ensuring smaller contractors can meet certification standards. However, these challenges are steadily being addressed through innovation and capacity building.
The introduction of modular fire systems allows older facilities to upgrade without full reconstruction, while digital monitoring tools make inspections more affordable and precise. Meanwhile, the expansion of local training programs ensures that every region in the Kingdom has access to qualified fire safety professionals.
These developments not only bridge technical gaps but also empower communities and industries to sustain a high standard of safety without compromising efficiency or cost-effectiveness.
Strategic Recommendations for Continuous Improvement
For Saudi Arabia to maintain its leadership in fire safety excellence, continuous improvement must remain central to its national strategy. The following priorities can help sustain progress:
- Encourage stronger collaboration between Civil Defense, private contractors, and educational institutions.
- Expand local manufacturing of NFPA-certified equipment to improve supply chain resilience.
- Integrate digital fire safety audits into smart city platforms to enhance monitoring and enforcement.
These measures, combined with ongoing training and public awareness, will ensure that NFPA compliance continues to evolve in step with technological and societal advancements.
Conclusion: Building a Safer Future Through Shared Commitment
The evolution of NFPA standards in Saudi Arabia represents far more than a regulatory achievement; it symbolizes a collective commitment to protecting lives, property, and progress. From fire alarm systems in modern skyscrapers to clean agent suppression in data centers, every application reflects a shared vision of safety built on knowledge, innovation, and responsibility.
DARS’s dedication to applying these standards across diverse industries highlights the importance of partnership in achieving national goals. Through precision in implementation, transparency in maintenance, and education across all levels, the company exemplifies the role that professional expertise plays in safeguarding the Kingdom’s future.
As Saudi Arabia continues its path toward global leadership in sustainable development, NFPA standards will remain the backbone of resilience ensuring that every structure built, and every life protected, stands as a testament to excellence and trust.




